Network Security has to evolve with the changing data security threats of today. Magarah designs security solutions with the latest technologies to keep your organization safe from malicious activity. More than ever before, network security must become application aware in order to mitigate application threats.
Magarah can build solutions to give companies complete control over applications, users and content. Combined with Role Based Access Control, our solutions will reduce the risks to any organization.
With our Managed Network Service, we are responsible for the configuration, monitoring and support of your network Services. Our technical teams look after the initial setup, the firewall security policy, VPNs, remote access, web filtering and application control.
Our solutions include
Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW) is, as Gartner defines it, a “deep-packet inspection firewall that moves beyond port/protocol inspection and blocking to add application-level inspection, intrusion prevention, and bringing intelligence from outside the firewall
Benefits of Using a Next Generation Firewall
The differentiating features of next generation firewalls create unique benefits for the companies using them.
NGFWs are able to block malware from entering a network, something that traditional firewalls would never be able to achieve.
They are better equipped to address Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
NGFWs can be a low-cost option for companies looking to improve their basic security because they can incorporate the work of antiviruses, firewalls, and other security applications into one solution.
The features of this include application awareness, inspection services, as well as a protection system and awareness tool that benefit the offering at all odds.
Magarah offers NGFWs provided by Gartner Leaders.
(NGIPS) Next Generation Intrusion Prevention System

The network IDPS market is composed of stand-alone physical and virtual appliances that inspect defined network traffic either on-premises or in the cloud. They are often located in the network to inspect traffic that has passed through perimeter security devices, such as firewalls, secure web gateways and secure email gateways.
While detection only (IDS) is still often used, a large number of appliances are deployed in-line and perform full-stream reassembly of network traffic. They provide detection via several methods —for example, signatures, protocol anomaly detection, behavioral monitoring and heuristics, advanced threat defense (ATD) integration, and threat intelligence (TI) to uncover unwanted and/or malicious traffic and report or take action on it.
All of the aforementioned methods augment IDPS capabilities with more context to reduce both the number of alerts as well as false-positives. False-positives are still a concern for clients when IDPSs are in blocking mode.
When deployed in-line, IDPSs can also use various techniques to detect and block attacks that are identified with high confidence; this is one of the primary benefits of this technology.
The capabilities of leading IDPS products have adapted to changing threats, and next-generation IDPSs
Secure Web Gateway
Secure Web gateway solutions protect Web-surfing PCs from infection and enforce company policies and filtering malicious internet traffic in real-time. At a minimum, a secure web gateway offers URL filtering, application controls for web applications and the detection and filtering of malicious code. Native or integrated data leak prevention is also increasingly included.
Secure Mail Gateway

Secure email gateways are comprehensive email security platforms designed to prevent web-based threats and ensure employee compliance.
The gateways funnel incoming email content through spam filters and scan content prior to allowing transport beyond a firewall.
These gateways include some kind of labeling or user governance system to identify malicious actors and prevent them from engaging in future communication.
Archiving capabilities within secure email gateways help businesses keep a record of prior communications for both compliance and reference purposes.
Benefits of Using a Next Generation Firewall
- Filter or scan mail for viruses, spam, or other malware
- Identify and block potentially dangerous content
- Securely encrypt communications
- Facilitate whitelisting or blocking capabilities to control suspicious accounts
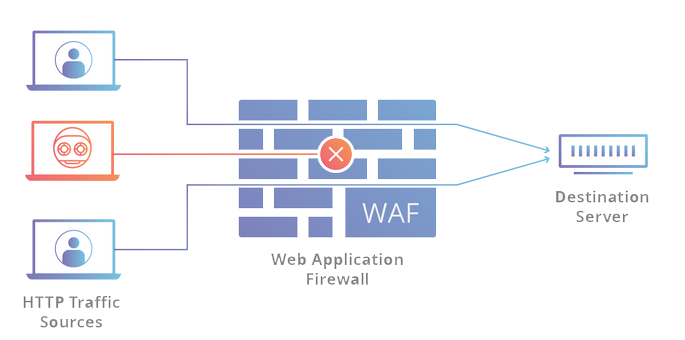
Web Application Firewall ( WAF )
Is an application firewall for HTTP applications. It applies a set of rules to an HTTP conversation. Generally, these rules cover common attacks such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection.
By deploying a WAF in front of a web application, a shield is placed between the web application and the Internet. While a proxy server protects a client machine’s identity by using an intermediary, a WAF is a type of reverse-proxy, protecting the server from exposure by having clients pass through the WAF before reaching the server.
A WAF operates through a set of rules often called policies. These policies aim to protect against vulnerabilities in the application by filtering out malicious traffic. The value of a WAF comes in part from the speed and ease with which policy modification can be implemented, allowing for faster response to varying attack vectors; during a DDoS attack, rate limiting can be quickly implemented by modifying WAF policies.